VoIP. Voice over IP. Voice over Internet Protocol.
All the same thing.
WARNING: Some language on this page can be considered high-tech. Proceed with caution.
Internet phone. Network phone. Cloud-based phone system. Hosted phone system. All terms tossed around to also mean VoIP.
Confused yet?
The simple way to put it – VoIP is taking your voice and transferring it over the internet vs. telephone circuits.
But VoIP is more than just that. It has the ability to merge voice and data applications, making business processes easier and faster. And it extends voice communication to anyone, anywhere, over any device.
VoIP can help to integrate all forms of communication.
Why should you care?
Because we said so. Kidding. Here’s the list:
- All phone service is moving in the direction of VoIP. POTS phone systems are obsolete. No new technology will be introduced there, so when it dies. It dies.
- Moving your calls to the internet means you get to use the network you already have in place, and no longer have to pay the phone company.
- You always get the latest and greatest features. Since the system is cloud based, it’s easy to maintain and upgrade.
- If you have internal systems already in place that you use to track customer data or other information, there’s a really good chance your VoIP system can communicate directly with it. This makes your phone calls even smarter!
- If you don’t have internal systems to collect or track data, then we have some pretty nifty tools to show you.
How your voice travels over the phone
TRADITIONAL (ANALOG) PHONE SYSTEM
When you talk on a traditional phone system, your voice vibrations get converted into an electromagnetic signal that can be carried over a telephone line, then converted back to audible sounds. A good example of this is the two tin cans with string between them. When talking into the can, and the string is tight, the voice vibrations travel from one can to the other. Same basic concept applies here. Your voice travels over telephone lines from point A to point B.

TRADITIONAL (ANALOG) PHONE SYSTEM
When you talk on a traditional phone system, your voice vibrations get converted into an electromagnetic signal that can be carried over a telephone line, then converted back to audible sounds. A good example of this is the two tin cans with string between them. When talking into the can, and the string is tight, the voice vibrations travel from one can to the other. Same basic concept applies here. Your voice travels over telephone lines from point A to point B.
To get a better feel for how old school phone systems and VoIP phone systems work, see the fancy diagrams below.
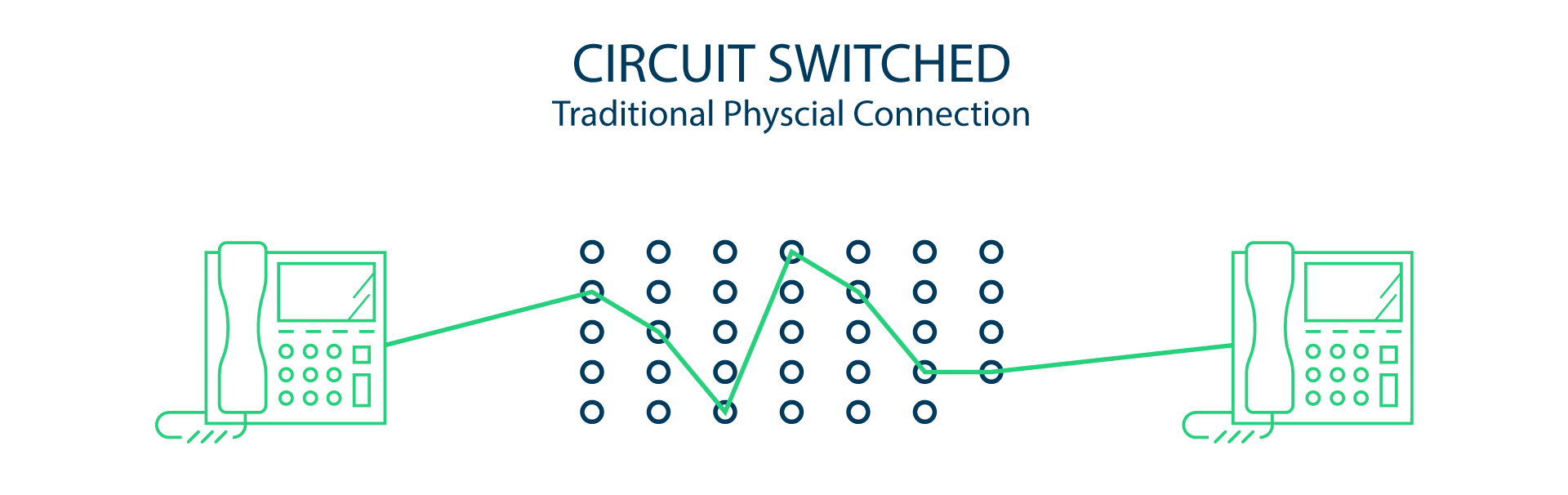
Circuit switched phone systems are physical connections from your phone, to the company telephone system, out to the phone companies network, then back to the person you are calling. Think of the old-school switchboards (which were all replaced by automatic exchanges in the 1960s). Because there is a lot of equipment involved, it was expensive to set up, and expensive to maintain. It also costs more money for phone calls to be routed this way. And if there was an issue with any of the telephone lines involved, the call would not go through.
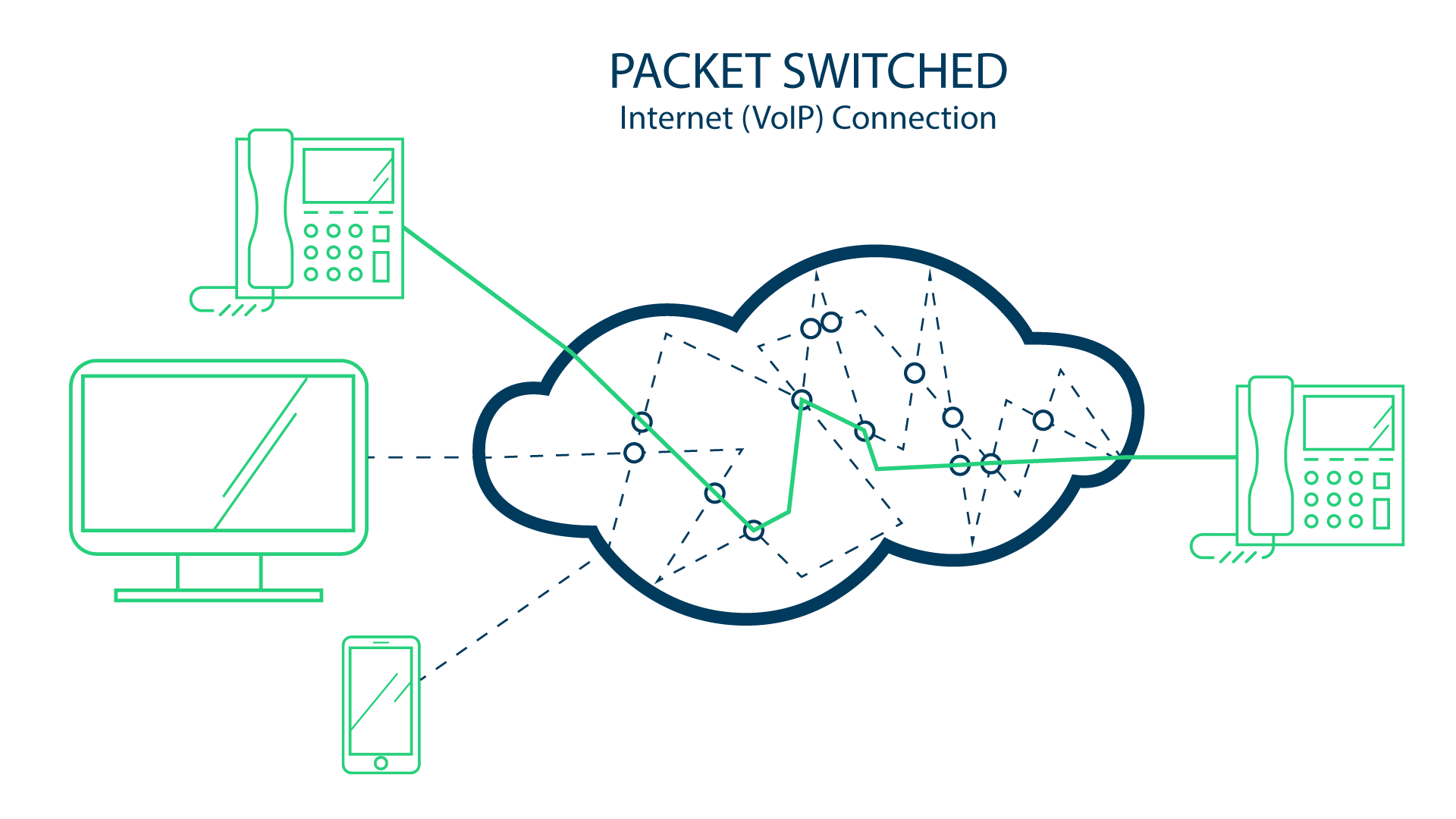
Packet switched connections use your existing internet or network for phone calls. So the digital information gets put in packets, goes up to the cloud and finds the best route to get to it’s destination. If there are any road blocks, the packets will find another route.
ACRONYMS
ATA | Analog Telephony Adapter
A device that converts analog voice signals (traditional telephone) to digital signals, which can then be transmitted over the Internet (VoIP).
CDR | Call Detail Record
Details about a specific call that includes origination, destination, day/time and duration.
DHCP | Dynamic Host Control Protocol
A client/server protocol that network administrators use to dynamically distribute IP addresses from a central point to each computer or device on a network.
DID | Direct Inward Dialing
A service that allows a company to give individual phone numbers to each person within its PBX system.
DNS | Domain Name System
A naming system for computers, services or other resources connected to the internet. Most often, it translates domain names to numerical IP addresses.
DSL | Digital Subscriber Line
Phone technology that allows a broadband internet digital connection to be carried over ordinary copper phone lines.
DTR | Data Transfer Rate
The speed that data can travel from one device to another. Generally measured in megabits or megabytes per second.
ISDN | Integrated Services Digital Network
A telephone system for digital transmission of voice and data over ordinary telephone copper wires.
ITSP | Internet Telephony Service Provider
A provider that uses your Internet connection to deliver telephone service.
IVR | Interactive Voice Response
Love or hate them, IVRs allow a computer to interact with humans using a telephone keypad or by speech recognition. Companies generally choose IVR systems when they receive large call volumes and need help with call flow.
LAN | Local Area Network
A computer network that links devices in a local area, such as a home, office, or group of buildings.
LNP | Local Number Portability
The ability to keep a phone number when switching to another telephone provider.
NAT | Network Address Translation
A method to use one public IP address to connect to the Internet and a set of local IP addresses to identify each PC or device in the local network.
PBX | Private Brand Exchange
A private telephone switching system used within a company. Users share a number of outside lines for making external phone calls.
POTS | Plain Old Telephone Service
A traditional analog phone line which was standard telephone service from 1876 to 1988.
PSTN | Public Switched Telephone Network
The world’s circuit-switched telephone networks.
RTP | Real Time Transport Protocol
A network protocol for delivering audio and video over IP networks.
SIP | Session Initiation Protocol
A communication protocol for Internet conferencing, telephony, and instant messaging. It is a request-response protocol, dealing with requests from clients and responses from servers.
SIP Trunking | Session Initiation Protocol Trunking
The use of VoIP to facilitate the connection of a PBX to the Internet.
TCP/IP | Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
A set of rules (protocol) over how information should be packed, sent and received over the internet.
VoIP | Voice over Internet Protocol
The transmission of voice over the Internet as digital packets rather than the traditional analog voice of the PSTN.
WLAN | Wireless Local Area Network
Communication between two or more computers, within a limited area, using radio communication to accomplish the same functionality that a wired LAN has.
